The Dolgoff Ethical Decision Making Model, developed by Ralph Dolgoff, provides a systematic approach to ethical decision-making. It is widely recognized for its comprehensiveness and practicality, offering a structured framework for individuals and organizations to navigate complex ethical dilemmas.
The model consists of four main elements: ethical values, ethical principles, ethical considerations, and ethical decision. These elements work together to guide decision-makers in identifying and evaluating ethical issues, considering relevant stakeholders, and arriving at morally sound conclusions.
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model: Dolgoff Ethical Decision Making Model
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model provides a structured framework for analyzing ethical dilemmas and making ethical decisions. The model is based on the following key principles:
- Identify the ethical issue.The first step in ethical decision-making is to identify the ethical issue or dilemma that is being faced.
- Gather relevant information.Once the ethical issue has been identified, it is important to gather all relevant information about the situation, including the facts, the values that are at stake, and the potential consequences of different decisions.
- Identify stakeholders.It is also important to identify all of the stakeholders who are affected by the ethical issue, and to consider their interests and perspectives.
- Develop and evaluate options.Once all of the relevant information has been gathered, the next step is to develop and evaluate different options for resolving the ethical issue. Each option should be evaluated based on its potential consequences, its impact on stakeholders, and its consistency with ethical principles.
- Make a decision.After all of the options have been evaluated, the final step is to make a decision about how to resolve the ethical issue. The decision should be based on the best available information and should be consistent with ethical principles.
The following diagram provides a visual representation of Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model:

Key Principles
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model is based on the following key principles:
- Autonomy:Individuals should be free to make their own choices and decisions, as long as those choices do not harm others.
- Beneficence:Actions should be taken to promote the well-being of others.
- Non-maleficence:Actions should not be taken that could harm others.
- Justice:Individuals should be treated fairly and equitably.
These principles can be used to guide ethical decision-making in a variety of situations.
Key Elements of the Model
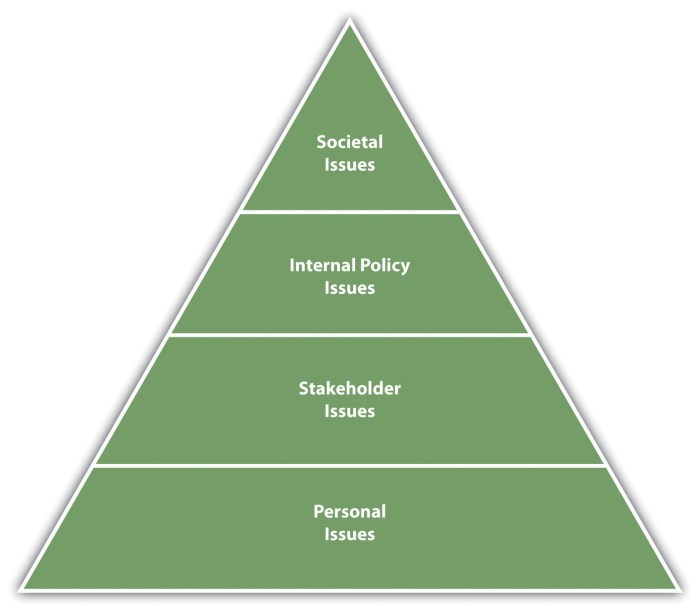
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model consists of four main elements: Ethical Values, Ethical Principles, Ethical Considerations, and Ethical Decision. These elements are interrelated and work together to guide individuals in making ethical decisions.
The model emphasizes the importance of considering multiple perspectives, values, and principles when making ethical decisions. It also highlights the need for careful consideration of the potential consequences of actions and the impact on stakeholders.
Ethical Values
Ethical values are fundamental beliefs about what is right and wrong. They are deeply ingrained in individuals and shape their moral compass. Some common ethical values include honesty, integrity, fairness, and respect for others.
Ethical values serve as the foundation for ethical decision-making. They provide a framework for individuals to evaluate the ethical implications of their actions and make choices that align with their moral principles.
Ethical Principles
Ethical principles are general rules or guidelines that guide ethical behavior. They are based on ethical values and provide more specific direction for making ethical decisions.
Some examples of ethical principles include the principle of autonomy (respect for individual self-determination), the principle of beneficence (doing good), and the principle of non-maleficence (avoiding harm).
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are specific factors or circumstances that need to be taken into account when making ethical decisions.
These considerations may include the potential impact on stakeholders, the legal implications, the cultural context, and the available resources.
Ethical Decision
The ethical decision is the final outcome of the ethical decision-making process. It is the choice that an individual makes after considering their ethical values, principles, and the relevant considerations.
The ethical decision should be based on sound reasoning and should align with the individual’s ethical principles and values.
Steps Involved in Using the Model
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model provides a structured approach to ethical decision-making. Applying the model involves several key steps:
Step 1: Identify the Ethical Issue, Dolgoff ethical decision making model
The first step is to clearly identify the ethical issue or dilemma at hand. This involves understanding the relevant facts, values, and stakeholders involved.
Example:A healthcare professional faces a dilemma in treating a patient who refuses life-saving treatment due to religious beliefs.
Step 2: Gather Relevant Information
Once the ethical issue is identified, gather all relevant information to inform the decision-making process. This may include consulting with experts, reviewing relevant policies, and considering the perspectives of stakeholders.
Example:The healthcare professional seeks guidance from medical ethics experts, reviews hospital policies, and discusses the situation with the patient’s family.
Step 3: Identify and Analyze Options
Next, identify and analyze the available options for addressing the ethical issue. This involves considering the potential consequences, both positive and negative, of each option.
Example:The healthcare professional considers options such as respecting the patient’s wishes, providing additional information to influence their decision, or involving a third party to facilitate a compromise.
Step 4: Make a Decision
After analyzing the options, make a decision that aligns with the identified ethical principles and values. This decision should be justified and supported by the information gathered and analysis conducted.
Example:The healthcare professional decides to respect the patient’s wishes, while providing ongoing support and resources to help them understand the consequences of their decision.
Step 5: Implement and Monitor the Decision
Once a decision is made, implement it in a manner that is consistent with the ethical principles and values. Monitor the outcomes of the decision to ensure that it is achieving the desired ethical outcomes.
Example:The healthcare professional provides the patient with resources and support, and monitors their condition to ensure their well-being.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Model
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model offers several strengths and weaknesses that influence its effectiveness in practical applications.
Strengths:
- Comprehensive Framework:The model provides a systematic and comprehensive framework that guides individuals through a structured process of ethical decision-making.
- Ethical Sensitivity:It emphasizes the importance of considering multiple ethical perspectives and values, fostering ethical sensitivity and awareness.
- Practicality:The model is designed to be practical and applicable in real-world situations, providing a step-by-step approach to ethical problem-solving.
Weaknesses:
- Complexity:The model’s comprehensive nature can make it complex and challenging to apply, especially in time-sensitive situations.
- Subjectivity:Ethical decision-making often involves subjective judgments, and the model does not fully account for the potential biases or personal values that may influence the outcome.
- Limited Applicability:The model may not be suitable for all ethical dilemmas, particularly those involving complex legal or technical considerations.
These strengths and weaknesses highlight the need for careful consideration when using Dolgoff’s model. Its comprehensive framework and ethical sensitivity make it a valuable tool for ethical decision-making, but its complexity and potential subjectivity should be recognized to ensure effective application.
Applications of the Model in Different Contexts
Dolgoff’s ethical decision-making model finds application in various fields and disciplines, enabling ethical considerations in diverse contexts. It offers a structured framework to guide decision-making processes, ensuring that ethical principles and values are taken into account.
Business Ethics
In business ethics, Dolgoff’s model assists in resolving ethical dilemmas encountered in corporate decision-making. It guides ethical conduct in areas such as employee relations, customer interactions, environmental sustainability, and financial transactions. By applying the model’s steps, businesses can identify ethical issues, consider stakeholder perspectives, and make choices that align with ethical values and principles.
Medical Ethics
Dolgoff’s model is extensively used in medical ethics to navigate complex ethical issues in healthcare settings. It provides a framework for decision-making in areas such as patient autonomy, informed consent, end-of-life care, and resource allocation. By incorporating ethical principles and stakeholder considerations, healthcare professionals can make informed and ethically sound decisions in challenging situations.
Environmental Ethics
Dolgoff’s model is applicable in environmental ethics, guiding decision-making processes related to environmental protection and sustainability. It helps stakeholders consider the ethical implications of actions on the environment, including the preservation of natural resources, pollution control, and climate change mitigation.
By applying the model, individuals and organizations can make choices that minimize environmental harm and promote ecological well-being.
Social Ethics
Dolgoff’s model extends to social ethics, aiding in addressing ethical dilemmas in areas such as social justice, human rights, and community development. It provides a structured approach to identifying and addressing social problems, considering the ethical implications of decisions and the impact on various stakeholder groups.
By applying the model, individuals and organizations can promote social equity, inclusion, and the well-being of society.
Comparison with Other Ethical Decision-Making Models
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model differs from other ethical decision-making models in several key ways. One of the main differences is that Dolgoff’s model is more focused on the individual and their own values, while other models may place more emphasis on the consequences of actions or the duties of individuals.
Utilitarianism
Utilitarianism is an ethical decision-making model that focuses on the consequences of actions and aims to maximize happiness or well-being. Dolgoff’s model, on the other hand, places more emphasis on the individual and their own values, rather than the consequences of actions.
Deontology
Deontology is an ethical decision-making model that focuses on the duties and obligations of individuals. Dolgoff’s model, on the other hand, is more focused on the individual and their own values, rather than the duties of individuals.
Virtue Ethics
Virtue ethics is an ethical decision-making model that focuses on the character and virtues of individuals. Dolgoff’s model, on the other hand, is more focused on the individual and their own values, rather than the character and virtues of individuals.
Case Studies and Examples
Dolgoff’s Ethical Decision-Making Model provides a structured framework for analyzing and resolving ethical dilemmas. It has been applied in various contexts, including business, healthcare, and public policy.
Here are some case studies and examples that demonstrate how Dolgoff’s model can be used to resolve ethical dilemmas:
Case Study: Marketing Campaign
A marketing team is developing a campaign for a new product. They are considering using a controversial advertising strategy that could potentially offend some consumers. The team members are divided on whether or not to proceed with the campaign.
Using Dolgoff’s model, the team can analyze the ethical implications of the campaign by considering the following factors:
- The potential impact on consumers
- The company’s reputation
- The legal implications
- The team’s own values
By carefully considering these factors, the team can make an informed decision about whether or not to proceed with the campaign.
Case Study: Healthcare Decision
A doctor is faced with a difficult decision about whether or not to perform a risky surgery on a patient. The patient has a low chance of survival, and the surgery could potentially cause further harm.
Using Dolgoff’s model, the doctor can analyze the ethical implications of the decision by considering the following factors:
- The patient’s wishes
- The patient’s family’s wishes
- The doctor’s own medical judgment
- The ethical principles of beneficence and non-maleficence
By carefully considering these factors, the doctor can make an informed decision about whether or not to perform the surgery.
Case Study: Public Policy Decision
A government official is faced with a decision about whether or not to support a new policy that could have a significant impact on the environment. The official is aware that the policy could have both positive and negative consequences.
Using Dolgoff’s model, the official can analyze the ethical implications of the decision by considering the following factors:
- The potential impact on the environment
- The potential impact on the economy
- The potential impact on society
- The official’s own values
By carefully considering these factors, the official can make an informed decision about whether or not to support the policy.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key principles of the Dolgoff Ethical Decision Making Model?
The key principles of the model include: considering multiple ethical perspectives, identifying relevant stakeholders, evaluating potential consequences, and seeking consensus among decision-makers.
How can the Dolgoff Model be applied in business ethics?
The model can guide businesses in making ethical decisions related to employee treatment, environmental impact, and customer relations.
What are the strengths and weaknesses of the Dolgoff Model?
Strengths include its comprehensiveness, flexibility, and applicability to various contexts. However, it may be time-consuming to apply and may not always provide clear-cut solutions.