Which of the following statements about bipolar disorder is true? This question sets the stage for an in-depth exploration of the complex nature of bipolar disorder. This multifaceted condition presents a unique set of challenges, and understanding its intricacies is paramount for effective management and support.
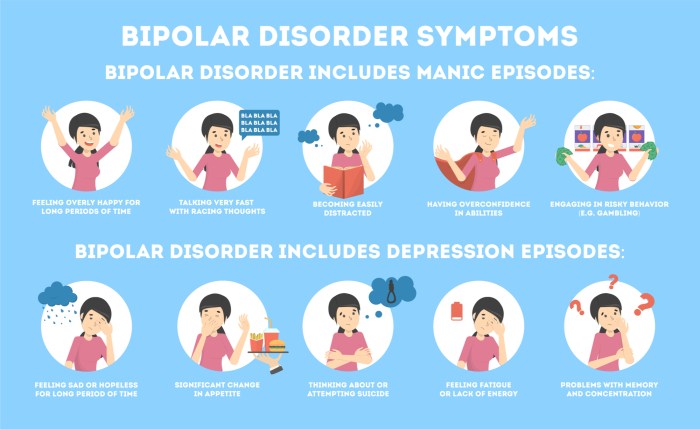
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition characterized by alternating episodes of mania or hypomania and depression. During manic or hypomanic episodes, individuals may experience elevated mood, increased energy, racing thoughts, and decreased need for sleep. In contrast, depressive episodes are marked by persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep, and feelings of worthlessness or guilt.
Prevalence and Diagnosis: Which Of The Following Statements About Bipolar Disorder Is True
Bipolar disorder is a mental illness characterized by alternating episodes of mania or hypomania and depression. It affects approximately 1% of the global population, with a lifetime prevalence of 2.8%.
Diagnostic Criteria
- Manic Episode:Elevated mood or irritability, inflated self-esteem, decreased need for sleep, racing thoughts, increased energy, and reckless behavior.
- Hypomanic Episode:Similar to a manic episode but less severe and not requiring hospitalization.
- Depressive Episode:Persistent sadness, loss of interest, changes in sleep or appetite, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of suicide.
Individuals must experience at least one manic or hypomanic episode and one depressive episode to be diagnosed with bipolar disorder.
Challenges in Diagnosis
Bipolar disorder can be difficult to diagnose, as its symptoms overlap with those of other mental illnesses, such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. Accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure appropriate treatment and prevent misdiagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of bipolar disorder is unknown, but it is believed to be a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and neurochemical factors.
Genetic Factors
- Bipolar disorder is highly heritable, with a genetic contribution estimated at around 80%.
- Specific genes and genetic mutations have been linked to an increased risk of developing the disorder.
Environmental Factors
- Childhood trauma, stress, and abuse can increase the risk of developing bipolar disorder.
- Substance abuse, particularly alcohol and cocaine, can trigger or worsen bipolar symptoms.
Neurochemical Factors
- Bipolar disorder is associated with imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
- Dysregulation of these neurotransmitters can lead to the extreme mood swings characteristic of the disorder.
Symptoms and Impact
Bipolar disorder is characterized by alternating episodes of mania or hypomania and depression. These episodes can vary in frequency, duration, and severity.
Manic and Hypomanic Episodes, Which of the following statements about bipolar disorder is true
- Elevated mood or irritability
- Inflated self-esteem
- Decreased need for sleep
- Racing thoughts
- Increased energy
- Reckless behavior
- Grandiose ideas
Depressive Episodes
- Persistent sadness
- Loss of interest
- Changes in sleep or appetite
- Fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Thoughts of suicide
Mixed Episodes
Mixed episodes occur when symptoms of both mania and depression are present simultaneously.
Bipolar disorder can have a significant impact on individuals, affecting their relationships, work, and overall well-being. Untreated bipolar disorder can lead to self-harm, substance abuse, and suicide.
Treatment and Management

Treatment for bipolar disorder aims to stabilize mood, prevent episodes, and improve overall functioning. A combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle interventions is typically recommended.
Medication
- Mood Stabilizers:Lithium, valproate, and carbamazepine are commonly used to stabilize mood and prevent episodes.
- Antipsychotics:Atypical antipsychotics, such as quetiapine and olanzapine, can be effective in treating mania and preventing relapse.
- Antidepressants:Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) can be used to treat depressive episodes.
Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to mood swings.
- Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT):IPSRT focuses on improving sleep-wake cycles, social rhythms, and interpersonal relationships.
- Family-Focused Therapy (FFT):FFT involves family members in the treatment process to provide support and improve communication.
Lifestyle Interventions
- Regular Sleep:Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help regulate mood and prevent episodes.
- Exercise:Regular physical activity can improve mood and reduce stress.
- Stress Management:Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help manage stress and prevent mood swings.
- Substance Avoidance:Avoiding alcohol and drugs is crucial for managing bipolar disorder, as substance abuse can trigger or worsen symptoms.
Prognosis and Outlook

The long-term prognosis for individuals with bipolar disorder varies depending on factors such as adherence to treatment, support systems, and severity of symptoms.
With appropriate treatment, most individuals with bipolar disorder can manage their symptoms and live fulfilling lives. However, it is important to note that bipolar disorder is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and support.
Adherence to Treatment
Adherence to treatment is crucial for managing bipolar disorder and preventing relapse. Individuals must take their medications as prescribed and attend therapy sessions regularly.
Support Systems
Strong support systems can play a vital role in recovery. Family members, friends, and support groups can provide emotional support, encouragement, and practical assistance.
Resources and Support Groups
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): https://www.nami.org
- Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance (DBSA): https://www.dbsalliance.org
- International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD): https://www.isbd.org
FAQ Resource
What are the symptoms of bipolar disorder?
Bipolar disorder is characterized by alternating episodes of mania or hypomania and depression. Symptoms of mania or hypomania include elevated mood, increased energy, racing thoughts, decreased need for sleep, and impulsive behavior. Symptoms of depression include persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep, and feelings of worthlessness or guilt.
How is bipolar disorder diagnosed?
Bipolar disorder is diagnosed based on a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional. The evaluation typically involves a detailed assessment of symptoms, personal and family history, and a physical examination to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
What are the treatment options for bipolar disorder?
Treatment for bipolar disorder typically involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle interventions. Medication can help stabilize mood and prevent episodes, while psychotherapy can help individuals manage symptoms, improve coping skills, and prevent relapse. Lifestyle interventions, such as regular sleep, exercise, and stress management, can also support treatment.