Which of these characteristics applies only to cardiac muscle tissue? This question unveils the unique properties that distinguish the heart’s muscular structure from all others. As we delve into this fascinating topic, we will discover the intricate mechanisms that govern the heart’s rhythm, coordination, and response to external stimuli.
Cardiac muscle tissue stands out among muscle types due to its exceptional characteristics, such as intercalated discs, autorhythmicity, and a distinct response to calcium ions. These features collectively orchestrate the heart’s vital functions, ensuring the uninterrupted pumping of life-sustaining blood throughout the body.
Definition of Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Cardiac muscle tissue is a specialized type of muscle tissue found exclusively in the heart. It exhibits unique characteristics that distinguish it from skeletal and smooth muscle tissues, enabling it to perform the vital function of pumping blood throughout the body.
Intercalated Discs
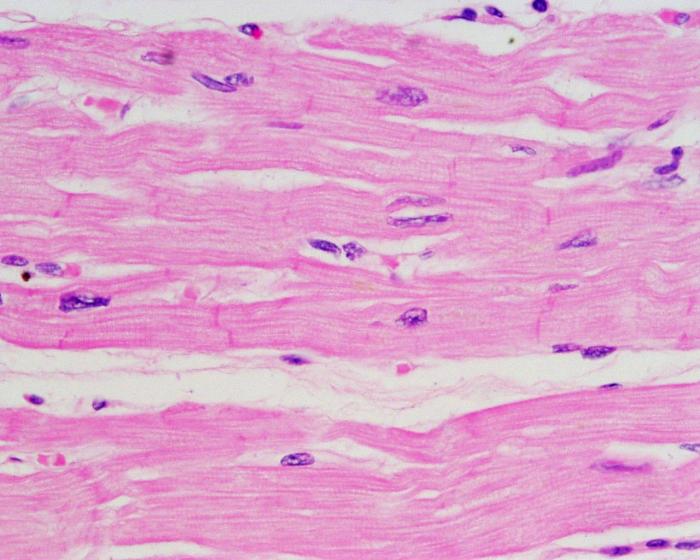
Structure and Function
Intercalated discs are specialized junctions between cardiac muscle cells that allow for the efficient transmission of electrical signals and mechanical coordination. These structures consist of desmosomes, which provide strong mechanical connections, and gap junctions, which facilitate the rapid spread of electrical impulses from one cell to the next.
Autorhythmicity
Intrinsic Ability to Generate Electrical Impulses
Cardiac muscle tissue possesses the unique ability to generate electrical impulses without external stimulation. This property, known as autorhythmicity, arises from the presence of specialized cells within the heart, primarily the sinoatrial (SA) node, which acts as the natural pacemaker of the heart.
Refractory Period
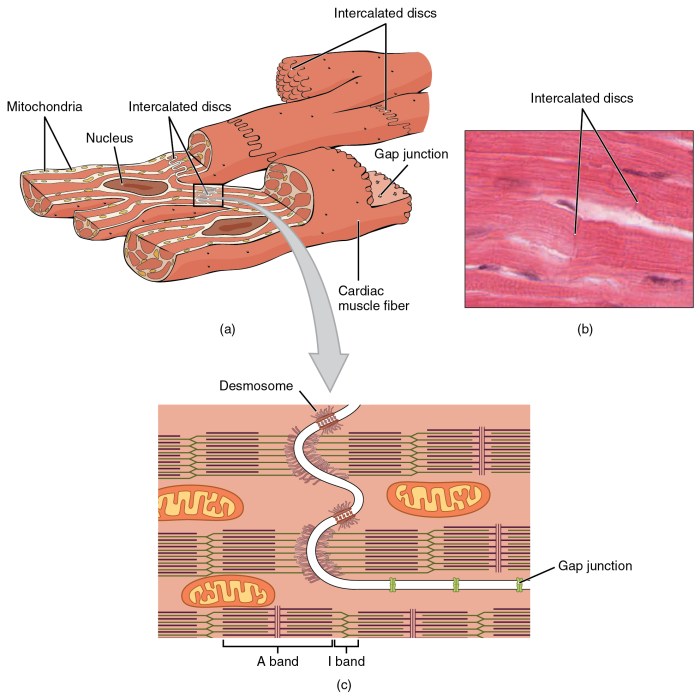
Preventing Tetanic Contractions and Ensuring Coordinated Heart Function
The refractory period is a period of time during which cardiac muscle tissue is unable to respond to a second electrical impulse. This property prevents tetanic contractions, allowing for a coordinated and rhythmic heartbeat. The refractory period is divided into two phases: the absolute refractory period, during which no response is possible, and the relative refractory period, during which a stronger-than-normal stimulus can elicit a response.
Response to Calcium
Triggering Muscle Contraction and Role of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Cardiac muscle tissue exhibits a unique response to calcium ions. Influx of calcium ions into the cell triggers muscle contraction. The sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle within cardiac muscle cells, plays a crucial role in calcium storage and release, facilitating the initiation and termination of muscle contraction.
Comparative Analysis with Skeletal and Smooth Muscle
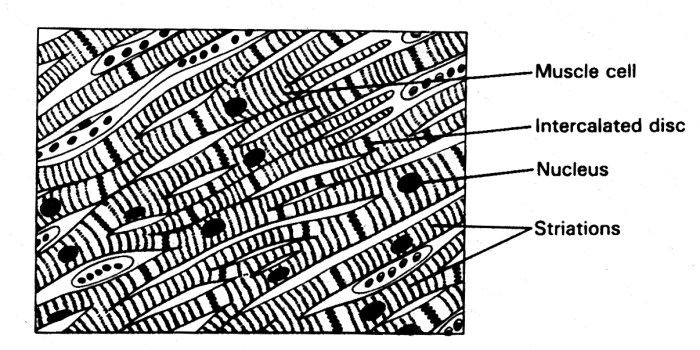
Key Characteristics and Distinguishing Features, Which of these characteristics applies only to cardiac muscle tissue
| Characteristic | Cardiac Muscle | Skeletal Muscle | Smooth Muscle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Heart | Attached to bones | Organs, blood vessels, respiratory tract |
| Cell Shape | Branched, striated | Long, cylindrical, striated | Spindle-shaped, non-striated |
| Intercalated Discs | Present | Absent | Absent |
| Autorhythmicity | Present | Absent | Present (to a lesser extent) |
| Response to Calcium | Triggers contraction | Triggers contraction | Regulates cell functions |
Question & Answer Hub: Which Of These Characteristics Applies Only To Cardiac Muscle Tissue
What is the significance of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle tissue?
Intercalated discs are specialized junctions that facilitate rapid and coordinated electrical signal transmission between cardiac muscle cells, enabling the heart to contract as a synchronized unit.
How does autorhythmicity contribute to heart function?
Autorhythmicity allows the heart to generate electrical impulses without external stimulation, ensuring a continuous and rhythmic heartbeat. The sinoatrial (SA) node acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses that spread throughout the heart.
What is the role of the refractory period in cardiac muscle tissue?
The refractory period prevents tetanic contractions by ensuring that cardiac muscle cells cannot respond to additional stimuli during a specific time interval after each contraction. This allows the heart to relax and refill with blood before the next contraction.